The Future of Farming: Aquaponics Farming 101
Aquaponics Farming: An Innovative Approach to Sustainable Agriculture
Are you interested in sustainable agriculture and want to learn more about Aquaponics Farming? You’ve come to the right place! In this blog post, we’ll explore the basics of Aquaponics Farming and why it’s gaining popularity as a sustainable farming method.
What is Aquaponics Farming?
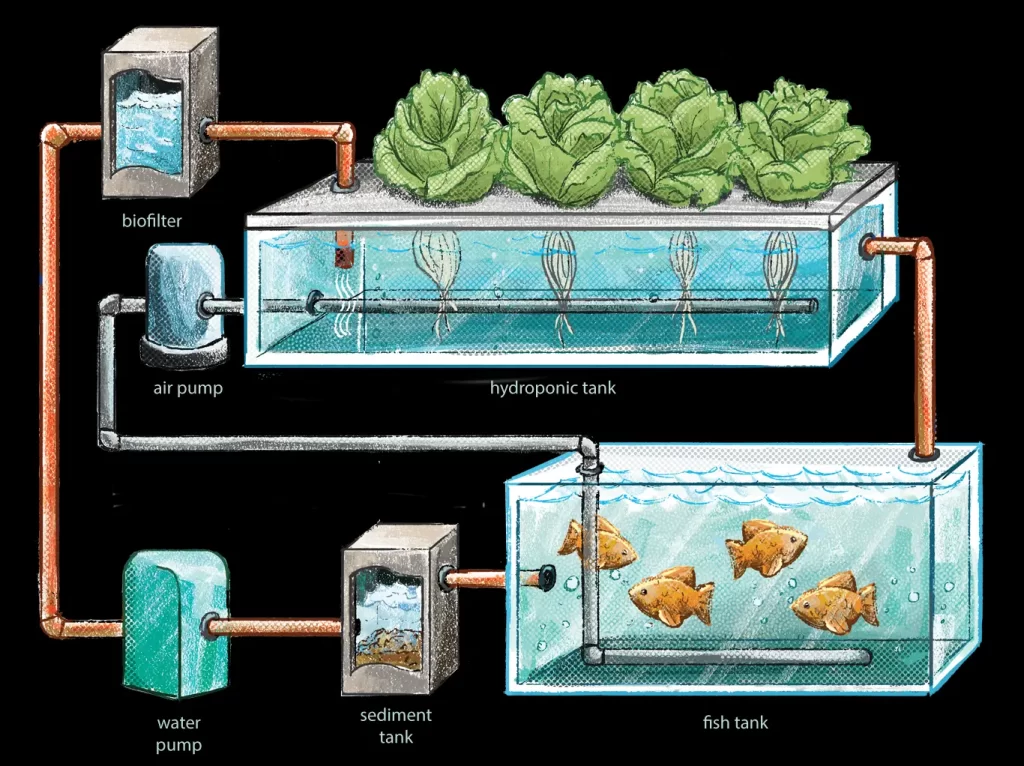
Aquaponics Farming is an innovative approach to sustainable agriculture that combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil) in a symbiotic system. In an aquaponics system, fish are raised in a tank, and their waste produces nutrients that feed the plants growing in a hydroponic bed. The plants, in turn, filter the water, which is then returned to the fish tank, creating a closed-loop system.

Benefits of Aquaponics Farming
Aquaponics Farming offers numerous benefits compared to traditional farming methods. Here are some of the most notable benefits:
- Water Efficiency: Aquaponics Farming uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming methods. The water in the system is continually recirculated, and the only water lost is through evaporation and transpiration by the plants.
- Sustainable: Aquaponics Farming is a sustainable farming method that doesn’t rely on synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. The system is entirely organic, and the fish waste provides all the nutrients needed for plant growth.
- Space Efficient: Aquaponics Farming can be done in a small space, making it ideal for urban areas where space is limited. It’s also an excellent option for those who want to grow their food but don’t have a lot of outdoor space.
- Versatile: Aquaponics Farming can be used to grow a wide variety of crops, including vegetables, fruits, and herbs. It’s also an excellent method for growing specialty crops that might be challenging to grow using traditional farming methods.
How Aquaponics Farming Works
Aquaponics Farming is a closed-loop system, which means that the water in the system is continuously recirculated. The fish produce waste that is rich in nutrients, which is then pumped through a filtration system to remove any solid waste. The filtered water is then pumped into the hydroponic bed, where the plants absorb the nutrients they need for growth.
As the plants absorb the nutrients, they also help to filter the water, removing any harmful chemicals or toxins. The clean water is then returned to the fish tank, completing the cycle.
The symbiotic relationship between the fish and the plants is what makes Aquaponics Farming such an efficient and sustainable farming method. The fish waste provides the nutrients that the plants need to grow, while the plants filter the water, creating a healthy environment for the fish to thrive.
Types of Aquaponics Systems
There are several types of Aquaponics systems, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. Here are some of the most common types:
- Media-based Aquaponics: This type of system uses a bed of grow media, such as gravel or clay pebbles, to support the plants. The media provides a surface area for beneficial bacteria to grow, which helps to break down the fish waste.
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Aquaponics: In an NFT system, a thin film of water is pumped over the roots of the plants, providing them with the nutrients they need to grow.
- Deep Water Culture (DWC) Aquaponics: DWC systems use floating rafts to support the plants, which are suspended in a nutrient-rich solution. This type of system is ideal for growing leafy greens and other fast-growing plants.
Disadvantages of Aquaponics Farming
While there are many advantages to aquaponics farming, there are also some disadvantages that should be considered before starting an aquaponics system. Some of the disadvantages of aquaponics farming include:
- Initial Investment Cost: Setting up an aquaponics system can be expensive, especially if you are starting with a larger system. There are many upfront costs to consider, including the cost of the fish tank, grow beds, pumps, and plumbing.
- Energy Use: Aquaponics systems require electricity to power pumps, heaters, and other equipment. Depending on the size of your system and your location, energy costs can be significant.
- Technical Expertise: Maintaining an aquaponics system requires technical expertise, including knowledge of water chemistry, fish care, and plant care. This can be a steep learning curve for beginners, and mistakes can be costly.
- Water Quality: In an aquaponics system, water quality is critical to the health of the fish and plants. Maintaining proper water quality requires regular monitoring and adjustment, which can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
- Fish Mortality: Fish can be sensitive to changes in water chemistry, temperature, and other factors. Disease outbreaks or other issues can lead to fish mortality, which can be costly for growers.
- Limited Crop Choices: While a wide variety of plants can be grown in an aquaponics system, some crops may not be suitable due to space limitations or other factors. This can limit the types of crops that can be grown and may affect the profitability of the system.
Overall, aquaponics farming has many advantages, but there are also some disadvantages to consider. Proper planning, research, and ongoing management are critical to ensuring the success and profitability of an aquaponics system.
Applications of Aquaponics Farming
Aquaponics Farming has numerous applications, including:
Commercial Farming: Aquaponics systems can be used to grow produce on a large scale, making it an excellent option for commercial farming operations.
Urban Farming: Aquaponics systems can be used to grow food in urban areas where space is limited, making it an excellent option for rooftop gardens and indoor farming operations.
Home Gardening: Aquaponics systems can be used to grow food at home, making it an excellent option for those looking to supplement their diet with fresh produce.
Is Aquaponics Sustainable?
Yes, Aquaponics Farming is a sustainable farming method that uses natural processes to grow plants and raise fish in a closed-loop system. It offers numerous benefits over traditional farming methods, including water efficiency, space efficiency, versatility, and organic production.
In Aquaponics Farming, the waste generated by fish is used to fertilize the plants, and the plants, in turn, clean the water for the fish. This creates a self-sustaining ecosystem that requires minimal inputs and produces minimal waste. The result is a highly efficient and sustainable farming system that can produce a significant amount of food in a small space.
Aquaponics Farming can also help to conserve water resources, as it uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming methods. This is because the water in the system is continuously recirculated, reducing the amount of water needed to grow the same amount of plants.
Overall, Aquaponics Farming is an innovative and sustainable farming method that has the potential to revolutionize the way we grow food. By using natural processes to create a self-sustaining ecosystem, Aquaponics Farming can help us to produce fresh, healthy food in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way.
Is Aquaponics Farming Profitable?
Aquaponics farming can be profitable, but the profitability depends on several factors such as the size of the system, the types of crops and fish being grown, the market demand for the products, and the cost of production.
Small-scale aquaponics systems can be profitable for niche growers who can charge a premium price for their products. These growers often sell their products locally, such as to farmers’ markets, restaurants, and CSA (Community Supported Agriculture) programs.
Large-scale aquaponics systems can also be profitable, but they require significant upfront investment costs, including land, equipment, and staffing. To be profitable, large-scale aquaponics farms need to have efficient systems in place that can produce high yields and reduce production costs.
The profitability of an aquaponics farm also depends on the types of crops and fish being grown. Some crops, such as leafy greens and herbs, can be grown in high volumes and can have a high market demand, making them a profitable choice for aquaponics growers. However, crops that require more space, such as tomatoes or cucumbers, may not be as profitable due to the limited space available in most aquaponics systems.
Overall, aquaponics farming can be profitable, but it requires careful planning, market research, and ongoing management to ensure that the system is producing high-quality products efficiently and cost-effectively.
What Crops Are Best for Aquaponics?
Aquaponics is a versatile farming method that can be used to grow a variety of crops, including vegetables, herbs, and even fruits. However, some crops are better suited for aquaponics systems than others. Here are some of the best crops for aquaponics:
- Leafy Greens: Leafy greens such as lettuce, kale, and spinach are some of the best crops for aquaponics because they grow quickly, have high yields, and don’t require a lot of space. These crops can be harvested continuously and are in high demand in the market.
- Herbs: Herbs such as basil, cilantro, and parsley are also well-suited for aquaponics systems. They grow quickly and have high market demand, making them a profitable choice for growers.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are a popular crop in aquaponics systems because they have high yields and can be grown vertically to maximize space. However, they require more attention to pruning and nutrient management than leafy greens or herbs.
- Cucumbers: Cucumbers are another popular crop in aquaponics systems. They have high yields and can be grown vertically, but they require more space than leafy greens or herbs.
- Strawberries: Strawberries can be grown in aquaponics systems and can have high yields if managed properly. They require more attention to pruning and nutrient management than other crops, but they can be profitable for growers.
Overall, the best crops for aquaponics are those that grow quickly, have high yields, and are in high market demand. Leafy greens, herbs, tomatoes, cucumbers, and strawberries are all good choices for aquaponics growers.
What Fish Is Best for Aquaponics?
There are several fish species that are well-suited for aquaponics, but the best fish species for your system will depend on several factors, including your location, climate, and personal preferences. Here are some of the most popular fish species for aquaponics:
- Tilapia: Tilapia is one of the most popular fish species for aquaponics because they are hardy, fast-growing, and can tolerate a wide range of water conditions. They are also a popular food fish and are in high demand in the market.
- Trout: Trout are another popular fish species for aquaponics because they grow quickly and have a high market value. However, they require colder water temperatures than tilapia, so they may not be suitable for all locations.
- Catfish: Catfish are a good choice for aquaponics because they are hardy, fast-growing, and have a high market value. They can also tolerate a wide range of water conditions.
- Perch: Perch are a good choice for aquaponics because they are hardy, fast-growing, and have a high market value. They are also tolerant of a wide range of water conditions.
Overall, the best fish species for aquaponics are those that are hardy, fast-growing, and can tolerate a range of water conditions. Tilapia, trout, catfish, and perch are all good choices for aquaponics fish farming, but there are many other fish species that can also be used successfully in aquaponics systems.
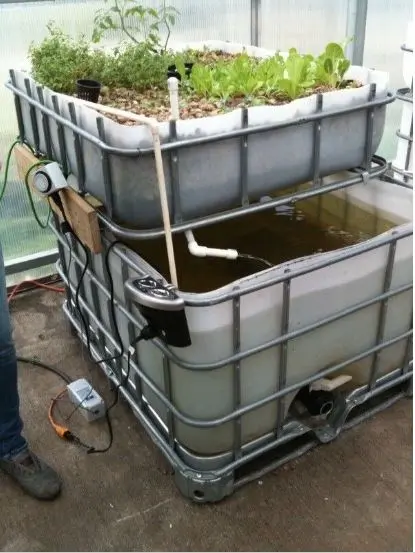
How to Build an Aquaponics Farming System
Building an aquaponics system can be a fun and rewarding project. Here are the basic steps for building a simple aquaponics system:
Step 1: Choose a Location
Choose a location for your aquaponics system that has a stable temperature, access to sunlight, and a level surface. You may want to consider building your system indoors or in a greenhouse to control the environment and protect your plants and fish from weather conditions.
Step 2: Gather Materials
You will need the following materials to build a simple aquaponics system:
• Fish tank
• Grow bed
• Water pump
• PVC pipes
• Fittings
• Gravel or hydroton
• Fish
• Plants
Step 3: Set Up the Fish Tank
Set up your fish tank in the location you have chosen. Fill it with water and add your fish.
Step 4: Set Up the Grow Bed
Place your grow bed above the fish tank. Connect the grow bed to the fish tank using PVC pipes and fittings. The water from the fish tank will be pumped up into the grow bed and then back down into the fish tank.
Step 5: Add Gravel or Hydroton to the Grow Bed
Fill the grow bed with gravel or hydroton. This will provide a medium for your plants to grow in and will also act as a biofilter, helping to remove waste from the water.
Step 6: Plant Your Plants
Plant your plants in the grow bed. You can grow a wide range of plants in an aquaponics system, from leafy greens to fruiting crops like tomatoes and cucumbers.
Step 7: Add the Water Pump
Add the water pump to the fish tank. The pump will circulate the water from the fish tank up to the grow bed and back down again.
Step 8: Monitor and Maintain Your System
Monitor your aquaponics system regularly to ensure that the water quality is good and the fish and plants are healthy. You may need to adjust the pH levels, add nutrients, and clean the system periodically.
Building an aquaponics system can be a fun and rewarding project. With a little bit of planning and effort, you can create a sustainable and self-sustaining ecosystem that produces fresh, healthy food. For more detailed instructions on how to build an aquaponics system, you can refer to online resources and guides.
Aquaponics Examples
Aquaponics is a versatile and innovative farming method that can be adapted to a wide range of settings and needs. Here are a few examples of how aquaponics is being used around the world:
- Urban Farming – Aquaponics is a popular farming method for urban farmers who want to grow fresh produce in limited space. In cities like New York and Chicago, urban farmers are using aquaponics systems to grow leafy greens, herbs, and other vegetables in small apartments and on rooftops.
- Commercial Agriculture – Aquaponics is also being used for large-scale commercial agriculture. In Australia, Sundrop Farms has built a 20-hectare greenhouse that uses solar energy and seawater to grow tomatoes using aquaponics. The system produces up to 17,000 tons of tomatoes per year and uses 90% less water than traditional agriculture methods.
- Community Gardens – Aquaponics is a great way to build community gardens that provide fresh produce to local residents. In the Philippines, the organization Gawad Kalinga has built community aquaponics gardens in low-income areas that provide fresh produce to local families and also serve as a source of income for community members.
- Research and Education – Aquaponics is being used in universities and research centers around the world to study sustainable farming practices and to teach students about agriculture and the environment. For example, the University of Arizona has an aquaponics research facility that studies the effects of different growing conditions on plants and fish.
- Home Gardening – Aquaponics can also be used for home gardening. There are many small-scale aquaponics systems available for purchase that are designed for home use. These systems can be used to grow herbs, vegetables, and even small fruits in your own backyard.
These are just a few examples of how aquaponics is being used around the world. As this innovative farming method continues to gain popularity, we can expect to see even more creative and impactful applications of aquaponics in the future.
In conclusion, Aquaponics Farming is an innovative and sustainable farming method that offers numerous benefits compared to traditional farming methods. Whether you’re interested in growing your food or want to start a small-scale commercial farm, Aquaponics Farming is an excellent option to consider. So why not give it a try and see what this innovative approach to sustainable agriculture can do for you?
